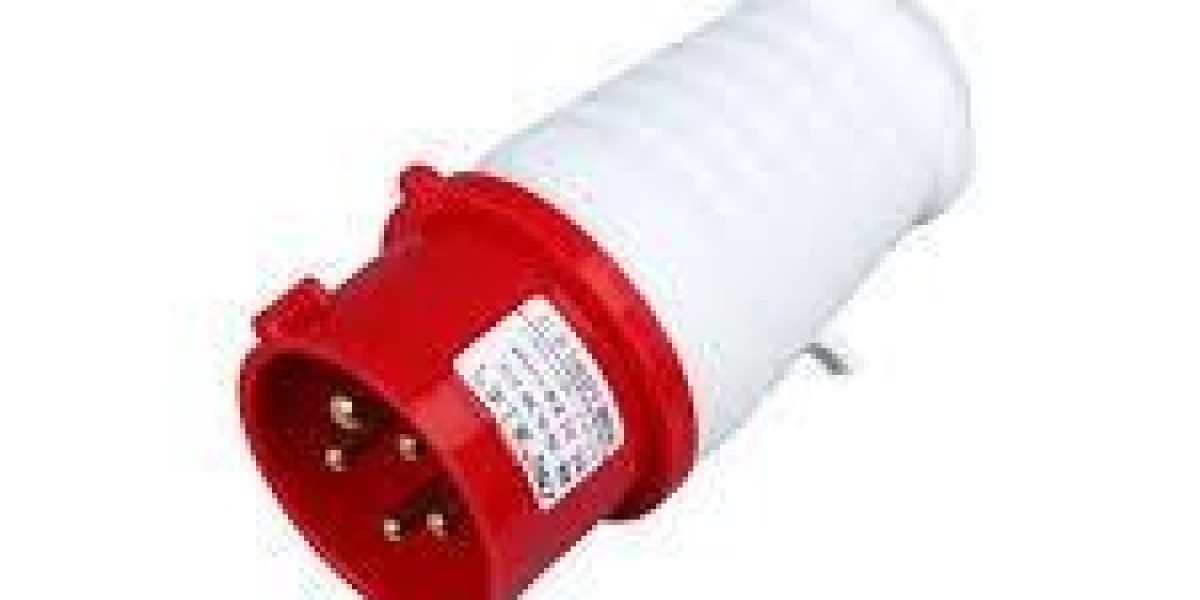
In heavy-duty installations the connector between a power source and equipment must be unambiguous in specification: the Industrial Plug is often chosen for its rugged contacts and clear coding, and the Industrial Plug should be specified with attention to contact metallurgy, mating cycles, and environmental sealing to avoid repeated failures. A robust connector strategy reduces downtime, simplifies spare management, and makes maintenance predictable — all essential when production cost is measured by minutes.
Match connector family to duty profile
Successful deployments begin by documenting how the connector will be used. Record expected continuous current, peak inrush, number of mates per shift, exposure to oils or chemicals, vibration spectrum, and ambient temperature range. These parameters determine contact cross-section, plating choice, insulator material, and coupling style (threaded versus bayonet). Overspecifying current ratings and choosing materials tested for the specific atmosphere prevents early thermal degradation and contact-resistance drift.
Contact metallurgy and plating choices
Long-term electrical performance hinges on metallurgy. Copper-alloy contact bodies with silver or nickel plating are common, but each plating has trade-offs: silver offers low initial resistance; nickel resists mechanical wear and high temperatures; gold flash on critical pins can mitigate fretting in corrosive atmospheres. Specify gas-tight or spring-loaded contacts where vibration and oxidation are concerns. Also ask suppliers for contact-resistance and mating-cycle test data relevant to your expected lifecycle.
Mechanical coupling, retention, and ergonomics
The coupling mechanism should match operational realities. Threaded couplings provide secure retention in vibrating environments but require more time to engage; bayonet or quick-lock systems speed repeated changes. Design panel cutouts and backing plates so mechanical loads transfer into structural elements, not into terminals. Ergonomic faceplates, clear keying, and tactile feedback reduce operator errors under time pressure and make field swapping faster and safer.
Sealing, ingress protection, and harsh environments
Match IP/NEMA ratings to the environment: IP66/67 for washdown and outdoor exposure; higher for submerged or pressure-wash situations. Ensure cable glands, O-rings, and shielded boots are specified and installed per torque recommendations so seals remain effective. For coastal, chemical, or sulfurous atmospheres choose corrosion-resistant housings and consult salt-spray and corrosion-test data. Proper sealing preserves both electrical performance and insulating integrity over years in the field.
Installation best practices that prevent recurring faults
Many connector failures are installation-related. Enforce calibrated crimp tooling, proper conductor sizing, and recorded torque settings during commissioning. Route strain-relieved cables to avoid axial stress on contacts, and maintain bend radii to prevent conductor fatigue. Perform an initial infrared thermal scan under representative load and document results — rerun scans after a short service period to spot settling issues. Clear labeling and wiring diagrams reduce human error during maintenance.
Modular accessories and retrofit planning
Select connector families that accept standard accessory modules — surge cassettes, locking collars, or telemetry plates — so upgrades and repairs avoid full-faceplate replacements. A retrofit-friendly footprint reduces downtime during modernization and simplifies spare inventories. Where possible, standardize across locations to minimize the number of SKUs technicians must carry and to speed training.
Testing, acceptance criteria, and lifecycle data
Insist on measurable acceptance criteria: contact resistance thresholds, thermal-rise limits, and mating-cycle validation under realistic conditions. Request vendor test reports and field-repair procedures. Archive commissioning tests alongside serial or location IDs to spot systemic trends. Lifecycle data allows procurement to prioritize repairable designs over sealed throwaway units, lowering total cost of ownership.
Spares strategy, readiness, and small-kits for rapid repair
Keep a compact kit of common inserts, gaskets, locking collars, and fastening hardware on site for fast swaps. Standardize connector families to limit SKUs and accelerate repairs. When a connector can be repaired by replacing an insert rather than the whole assembly, mean time to repair drops and waste decreases. Train technicians on quick-swap procedures and torque audits to maintain consistent connection quality.
Monitoring and predictive maintenance opportunities
Small sensors — temperature probes at contact points, outlet current monitors, or insertion counters — turn connectors into early-warning nodes. Provide mounting bosses and wiring channels in initial installations so telemetry can be added with minimal rework. Trend analysis of resistance or temperature data often reveals gradual degradation before functional failure.
A disciplined approach to specifying, installing, and maintaining heavy-duty connectors reduces unplanned stops and extends equipment life. Prioritize correct contact metallurgy, robust mechanical design, proper sealing, and a pragmatic spare-parts plan to keep operations running smoothly. For technical notes and product details, visit https://www.nante.com/news/industry-news/what-is-industrial-plug.html