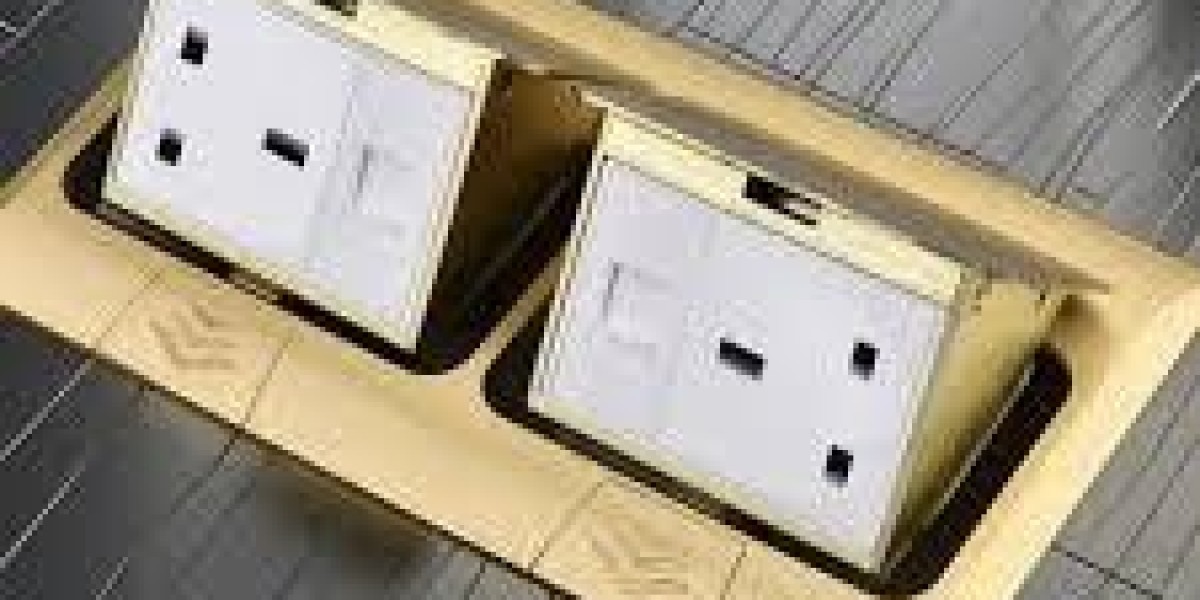
Good installations start with clear intent: on many sites a Socket Box is placed where service access, cord reach, and visual inspection converge, and experienced teams know that selecting the right Socket Box during design prevents costly retrofits and improves day-to-day reliability. This article walks through practical decisions—site assessment, materials, installation discipline, modular spares, and maintenance planning—so facility managers and installers can specify enclosures that stay serviceable and predictable for years.
Site assessment: match the enclosure to real exposures
Begin with a concise survey that documents the micro-environment. Note direct rainfall, irrigation spray, pressure-washing, chemical exposure, UV levels, airborne particulates, mechanical impact risk, and human traffic. Record expected cleaning regimes and temperature swings. These specifics translate directly into required IP/IK ratings, gasket chemistry, fastener metallurgy, and mounting clearances. Also identify likely future tasks — metering, temporary power taps, or monitoring — so the enclosure’s internal volume and knockouts won’t be limiting later upgrades.
Materials, coatings, and sealing choices
Material selection determines long-term resilience. UV-stabilized polymers resist fading and embrittlement; powder-coated aluminum provides a balance of weight and strength; 316 stainless is appropriate for coastal or chemical environments. Choose gasket compounds (silicone, EPDM, nitrile) to resist local cleaning agents and temperature ranges. Specify captive fasteners, raised sealing channels, and recessed lid designs to protect gaskets from abrasion when covers are opened repeatedly. When dissimilar metals are used, call out compatible plating to avoid galvanic corrosion — a frequent cause of early failures.
Installation practices that preserve ingress protection
Good product specs are wasted without disciplined installation. Prepare mounting surfaces so they are flat and clean; uneven mating faces compress gaskets unevenly and invite leaks. Follow manufacturer torque values for lid screws and cable glands — overtightening can deform seals while under-torquing allows ingress. Create drip loops outside entries, and position cable entries to discourage water tracking toward seams. Use the correct gland sizes and install proper strain relief so cable movement does not translate into terminal stress. Record torque values and wiring diagrams at handover as part of the as-built package.
Nante accessory ecosystem and modular interiors
Select enclosures that accept removable mounting plates, DIN-rail frames, and swappable insert modules so a single failed component — a breaker, meter, or surge protector — can be changed without disturbing adjacent circuits. Vendors that publish compatibility matrices and standardized spare kits (gaskets, common inserts, gland sets) shorten repair time and reduce spare inventory complexity. Consider standardizing on a modular accessory ecosystem to enable technicians to complete most fixes on one visit, especially across multi-site portfolios.
Thermal, moisture control, and simple monitoring
Even well-sealed enclosures can suffer from heat buildup or condensation. Arrange heat-dissipating devices away from sensitive electronics and use thermally conductive mounting plates when necessary. For condensation-prone sites, filtered breathers, desiccant holders, or low-wattage thermostatic heaters help manage moisture while preserving ingress ratings. For mission-critical circuits, reserve space and power for modest sensors (temperature, humidity, lid-open) so teams receive early warnings about failing seals or thermal excursions — inexpensive telemetry that averts disruptive outages.
Inspection routines and spare-part planning
Create a short, repeatable checklist: verify gasket compression, confirm gland and terminal torque, inspect for corrosion or mechanical damage, and measure contact resistance on essential circuits. Schedule checks after severe weather events and maintain a compact on-site kit with common gaskets, inserts, and gland sizes to enable same-day repairs. Log replacements and observed wear to forecast reorder points and to support lifecycle budgeting. Treat spare parts as consumables with reorder thresholds informed by real field data.
Security, aesthetics, and public-facing considerations
For public or semi-public installations, balance access with deterrence. Lockable lids, tamper-resistant fasteners, recessed anchors, and low-gloss finishes reduce theft and vandalism while preserving serviceability for authorized crews. Provide external labeling and a small weatherproof document pouch with wiring diagrams to let technicians perform quick visual checks without opening the enclosure.
A well-specified and carefully installed enclosure that matches materials to exposure, enforces installation discipline, and supports modular spare strategies will provide reliable service and lower lifecycle costs. For product datasheets, accessory lists, and installation guidance from Nante, visit www.nante.com